What Are TDD and THD? — A Comprehensive Explanation of Harmonic Distortion Indicators
In power systems and power quality management, harmonic distortion is a crucial issue that cannot be ignored. Two key indicators used to measure harmonic distortion are THD (Total Harmonic Distortion) and TDD (Total Demand Distortion). These terms are commonly referenced in technical specifications and serve as essential benchmarks in the design, operation, and maintenance of power systems.
THD (Total Harmonic Distortion)
Definition
THD refers to the percentage representation of harmonic currents or voltages relative to the fundamental wave. It quantifies the proportion of harmonic components in the waveform. The formula for calculation is:
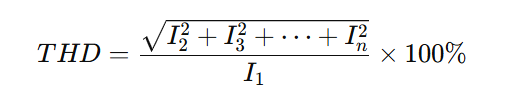
Where:
I1 is the fundamental current,
I2, I3,In are the harmonic currents.
Significance
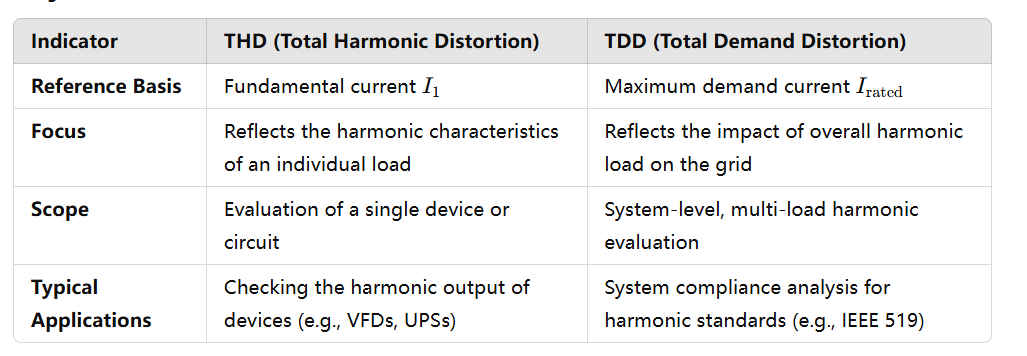
THD is primarily used to measure the degree of harmonic distortion in a specific load. It directly correlates with the particular load or power quality, serving as an important indicator of equipment performance and power quality.
Application Scenarios
THD is more suitable for assessing the harmonics of a single device or specific circuit. For example:
- Checking the harmonic content of a variable frequency drive (VFD);
- Testing the output voltage quality of an uninterruptible power supply (UPS).
---
TDD (Total Demand Distortion)
Definition
TDD refers to the ratio of total harmonic current to the maximum demand current of the system (usually the rated current or maximum load of the transformer), reflecting the overall impact of harmonic distortion on the grid. The calculation formula is:
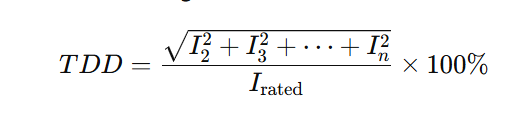
Where:
Irate is the rated current or maximum demand current of the system.
Significance
TDD emphasizes the impact of harmonic loads on the entire system and is more suitable for assessing the harmonic level under multi-load operating conditions, closely associated with system capacity.
Application Scenarios
TDD is more suitable for system-level harmonic analysis, such as:
- Total harmonic load evaluation when multiple devices are running on the grid;
- Determining whether the grid complies with harmonic standards (e.g., IEEE 519-2014 requirements).
---
Key Differences Between THD and TDD
How to Reduce THD and TDD?
Methods to reduce harmonic distortion mainly include:
1. Install Harmonic Mitigation Devices
- Active Harmonic Filters (AHF): Real-time monitoring and compensation of harmonics.
- Static Var Generators (SVG): Improve power factor and optimize harmonics.
2. Choose Low Harmonic Devices
Use power equipment that complies with international harmonic standards (e.g., IEEE 519 or GB/T 14549).
3. Optimize System Design
- Increase system capacity to reduce the proportional impact of harmonics;
- Properly configure loads to prevent harmonic sources from accumulating.
4. Regular Monitoring and Maintenance
Continuously track THD and TDD using harmonic analyzers or power quality monitoring equipment, and make timely adjustments.
---
Conclusion
THD and TDD are two important indicators for measuring harmonic distortion, each with its focus and applicable scope. THD is better suited for individual device or circuit analysis, while TDD is used for system-level harmonic evaluation. By effectively utilizing these two indicators, one can significantly improve the stability and efficiency of power systems.
If you are looking for effective harmonic mitigation solutions, consider YT Electric's Active Harmonic Filter (AHF) and Static Var Generator (SVG), which can help you manage harmonic and reactive power compensation efficiently and reliably.
Subscribe to us to enjoy event prices and get some of the best prices.
 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported

