Film capacitors, known for their reliability, longevity, and stability, have become essential components in modern electronics. They are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery and renewable energy systems. Their unique structure and performance characteristics make them an ideal choice for various demanding environments.
1. What Are Film Capacitors?
Film capacitors, also known as plastic film capacitors, are a type of capacitor where the dielectric material is a thin film of plastic. The plastic film is coated with metal, and the electrodes are typically made of aluminum or zinc. These capacitors are manufactured by winding the metallized film into cylindrical rolls or stacking it into layered structures, then encapsulated to ensure protection from environmental factors.
Film capacitors are known for their excellent electrical characteristics, such as low equivalent series resistance (ESR), low dielectric losses, and high insulation resistance. They come in various shapes and sizes, tailored to different applications, making them versatile in the world of passive components.
2. Basic Working Principle of Film Capacitors
Like all capacitors, film capacitors store electrical energy by accumulating charge on two conductive plates (electrodes) separated by a dielectric material (the film). When a voltage is applied across the capacitor, an electric field is generated across the dielectric, causing electrons to accumulate on one plate and leave the other plate. The amount of energy stored depends on the capacitance, which is a function of the surface area of the electrodes, the distance between them, and the dielectric constant of the material used.
The formula to calculate the capacitance of a film capacitor is:
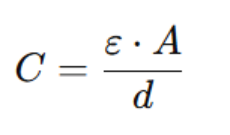
Where:
· C is the capacitance,
· ε is the dielectric constant of the film,
· A is the area of the electrodes,
· d is the thickness of the dielectric film.
3. Types of Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are available in various types based on the type of dielectric material used and their construction. Some common types include:
3.1. Metallized Film Capacitors
Metallized film capacitors use a very thin layer of metal deposited onto the plastic film, which serves as the electrodes. These capacitors are compact and self-healing, meaning that if a breakdown occurs at a weak point in the dielectric, the affected area vaporizes without damaging the rest of the capacitor. This makes metallized film capacitors highly reliable and suitable for applications where long-term stability is crucial.
3.2. Foil Film Capacitors
In foil film capacitors, separate metal foils are used as electrodes, and the dielectric film is placed between them. These capacitors are more robust and can handle higher current loads than metallized film capacitors. However, they tend to be bulkier, and unlike metallized versions, they do not offer self-healing properties.
3.3. Polyester Film Capacitors
Polyester (PET) film capacitors are one of the most widely used types of film capacitors due to their cost-effectiveness and reliable performance. They offer good temperature stability and high capacitance values in compact packages. However, polyester capacitors tend to have higher dielectric losses and ESR compared to other film capacitors, which limits their use in high-frequency applications.
3.4. Polypropylene Film Capacitors
Polypropylene (PP) film capacitors are known for their excellent electrical characteristics, such as low dielectric loss, low ESR, and high insulation resistance. They are particularly well-suited for high-frequency applications and are commonly used in power electronics, RF circuits, and audio equipment.
3.5. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Film Capacitors
PTFE film capacitors (also known as Teflon capacitors) offer outstanding electrical performance with very low dielectric loss and excellent temperature stability. They are used in extremely demanding applications, such as high-frequency RF and microwave systems. However, they are more expensive than other film capacitors, limiting their use to specialized applications.
4. Advantages of Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are widely favored in the electronics industry for several key reasons. Their advantages include:
4.1. Long Life and High Reliability
One of the most significant advantages of film capacitors is their long operational life. The materials used in their construction—mainly the plastic film dielectric and metallized electrodes—are resistant to environmental factors such as moisture and heat, ensuring stable performance over long periods. Additionally, the self-healing property of metallized film capacitors enhances their durability, as minor dielectric breakdowns are corrected without causing failure.
4.2. Low ESR and Dielectric Loss
Film capacitors typically have very low ESR and dielectric loss, making them highly efficient. This is particularly beneficial in high-frequency applications where energy losses can affect the overall performance of the circuit. The low loss factor makes them suitable for applications like power factor correction, high-quality audio circuits, and RF transmission.
4.3. High Insulation Resistance
Film capacitors exhibit high insulation resistance, preventing leakage currents and improving overall circuit efficiency. This characteristic is essential in applications where minimal energy loss is critical, such as timing circuits and precision analog circuits.
4.4. Thermal Stability
Film capacitors are known for their excellent thermal stability, maintaining consistent capacitance values over a wide temperature range. This makes them ideal for applications that require reliable performance under varying environmental conditions, such as automotive electronics and industrial machinery.
4.5. Self-Healing Capability
Metallized film capacitors possess a unique self-healing capability. When a dielectric breakdown occurs, the affected area vaporizes, isolating the fault and preventing further damage to the capacitor. This feature ensures that the capacitor can continue to function even after experiencing minor electrical stress, extending its lifespan and improving reliability.
5. Applications of Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are used in a wide range of applications across different industries, including automotive, telecommunications, consumer electronics, and industrial systems. Some common applications include:
5.1. Power Factor Correction
Film capacitors are widely used in power factor correction (PFC) systems, where they help improve the efficiency of electrical systems by reducing reactive power consumption. Their low loss characteristics make them ideal for use in both low-voltage and high-voltage PFC applications, such as in industrial power grids and renewable energy installations.
5.2. Power Electronics
Film capacitors play a critical role in power electronics, particularly in smoothing, filtering, and decoupling tasks. In inverter circuits, for instance, they help smooth the output voltage and filter out unwanted high-frequency noise. Their ability to handle high currents and voltages while maintaining stability and low losses makes them indispensable in power converters and motor drives.
5.3. Audio Equipment
High-quality audio circuits rely on film capacitors for their low distortion and stable performance across a wide frequency range. Polypropylene film capacitors are particularly popular in audiophile-grade equipment due to their low dielectric loss and excellent sound fidelity, ensuring that audio signals are transmitted with minimal degradation.
5.4. Telecommunications
Film capacitors are also used in telecommunications equipment, where they are employed in signal filtering, voltage stabilization, and impedance matching. Their reliability and ability to perform consistently in high-frequency environments make them suitable for use in communication networks, radio systems, and data transmission equipment.
5.5. Automotive Electronics
In the automotive industry, film capacitors are used in various applications, from onboard electronics to electric vehicles (EVs). They are found in power management systems, motor control units, and battery management systems, where their high reliability and thermal stability ensure optimal performance under the harsh conditions often encountered in automotive environments.
5.6. Renewable Energy Systems
As the world moves toward cleaner energy sources, film capacitors have found their place in renewable energy systems, such as wind turbines and solar inverters. These capacitors are used to filter and smooth the electrical output from these systems, ensuring stable energy delivery to the grid or storage systems.
6. The Future of Film Capacitors: Trends and Innovations
The film capacitor market is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in materials science and growing demand in emerging sectors such as renewable energy, electric vehicles, and 5G telecommunications. Several trends and innovations are shaping the future of film capacitors:
6.1. Miniaturization and High-Density Designs
As electronic devices continue to shrink in size, there is increasing demand for smaller capacitors with higher capacitance values. Manufacturers are developing thinner dielectric films and more compact designs to meet the need for high-performance capacitors in space-constrained applications.
6.2. Higher Temperature Tolerances
With the rise of electric vehicles and renewable energy systems, there is a growing need for capacitors that can operate reliably at higher temperatures. Advances in dielectric materials are enabling the development of film capacitors that can withstand temperatures beyond 125°C, making them suitable for harsh environments.
6.3. Improved Energy Efficiency
The demand for energy-efficient electronics is driving innovation in film capacitor technology. Manufacturers are focusing on reducing ESR and dielectric losses even further to improve overall system efficiency. This is particularly important in power electronics, where every bit of energy saved can result in significant cost reductions and improved system performance.
6.4. Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Materials
As sustainability becomes a priority in the electronics industry, there is a growing focus on using eco-friendly materials in capacitor manufacturing. Biodegradable or recyclable dielectric materials are being explored as alternatives to traditional plastics, reducing the environmental impact of capacitor production and disposal.
Film capacitors have proven to be a versatile and reliable component in a wide range of electronic applications. Their low ESR, long life, high insulation resistance, and self-healing capabilities make them an ideal choice for demanding environments such as automotive electronics, power electronics, and renewable energy systems.
As technology advances, film capacitors are evolving to meet the challenges of emerging industries, offering higher performance in smaller, more efficient packages. With ongoing innovations in materials science and manufacturing techniques, film capacitors will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of electronics.

Subscribe to us to enjoy event prices and get some of the best prices.
 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported

